TypeScript
Nội dung được dịch từ typescriptbook.jp
Cuốn sách "Survival TypeScript" này là sách nhập môn dành cho các developer sử dụng TypeScript trong công việc thực tế. Trang này là bản tóm tắt các nội dung chính từ hàng trăm trang của cuốn sách, giúp bạn nắm bắt nhanh nhất các đặc điểm của TypeScript.
» Tìm hiểu thêm về cuốn sách
» Muốn viết TypeScript ngay bây giờ
TypeScript là gì
- Ngôn ngữ lập trình là superset của JavaScript.
- Là ngôn ngữ kiểu tĩnh, có thể kiểm tra tĩnh tính đúng đắn của chương trình.
- Có hệ sinh thái phong phú với nhiều library và IDE hỗ trợ phát triển.
- Được Microsoft phát triển năm 2012 và công bố dưới dạng mã nguồn mở.
» Tìm hiểu thêm về đặc điểm của TypeScript
» Tìm hiểu thêm về bối cảnh ra đời của TypeScript
TypeScript là Superset của JavaScript
- Superset là ngôn ngữ được tạo ra bằng cách mở rộng ngôn ngữ gốc, đồng thời duy trì tính tương thích với ngôn ngữ gốc.
- TypeScript là ngôn ngữ được tạo ra bằng cách mở rộng JavaScript, đồng thời duy trì tính tương thích với JavaScript.
- Do đó, mọi code JavaScript đều có thể được xử lý như TypeScript.
- TypeScript bổ sung các tính năng riêng như type annotation, interface, generics.
Lợi ích của Superset
- Dễ học: Có thể tận dụng kiến thức JavaScript để học TypeScript.
- Tận dụng tài sản có sẵn: Có thể phát triển dựa trên code JavaScript hiện có.
- Dễ chuyển đổi: Các dự án JavaScript hiện có có thể dễ dàng chuyển sang TypeScript.
» Tìm hiểu thêm về mối quan hệ giữa TypeScript và JavaScript
Kiểm tra tĩnh
- TypeScript có thể kiểm tra tĩnh tính đúng đắn của chương trình.
- JavaScript phải chạy chương trình mới biết có bug hay không.
- TypeScript có thể kiểm tra mà không cần chạy chương trình.
» Tìm hiểu thêm về kiểm tra tĩnh
Nâng cao hiệu quả phát triển, chất lượng và sự an tâm
- Phát hiện vấn đề sớm, tăng hiệu quả phát triển.
- Phát hiện và sửa lỗi ngay khi viết code, ngăn ngừa bug.
- Khi tích hợp editor với TypeScript, có thể kiểm tra realtime và code completion.

- Việc sửa lỗi sớm giúp tăng độ tin cậy và sự an tâm cho sản phẩm.
- Kiểm tra tĩnh là yếu tố an tâm quan trọng khi phát triển các chương trình lớn, khó nhìn thấy tổng thể, hoặc các hệ thống quan trọng.
Cơ chế kiểm tra
- Kiểm tra của TypeScript dựa trên hệ thống kiểu (type system).
- Dựa trên hệ thống kiểu, chương trình được kiểm tra tại thời điểm compile.
Hệ thống kiểu
- Hệ thống kiểu gán kiểu cho mỗi loại dữ liệu và đặt ra các ràng buộc về thao tác có thể thực hiện trên dữ liệu đó.
- Nhờ đó, đảm bảo rằng chỉ các giá trị được chỉ định mới được gán cho biến và chỉ các thao tác được chỉ định mới được thực hiện, giúp chương trình chính xác và an toàn hơn.
- Hệ thống kiểu được xây dựng dựa trên "lý thuyết kiểu" trong toán học, có thể phát hiện lỗi chương trình thông qua chứng minh toán học.
Type annotation
- Kiểu (type) là thứ ràng buộc giá trị nào có thể được gán cho biến.
- Developer chỉ định kiểu của biến thông qua type annotation.
- Trong TypeScript, kiểm tra được thực hiện dựa trên type annotation.
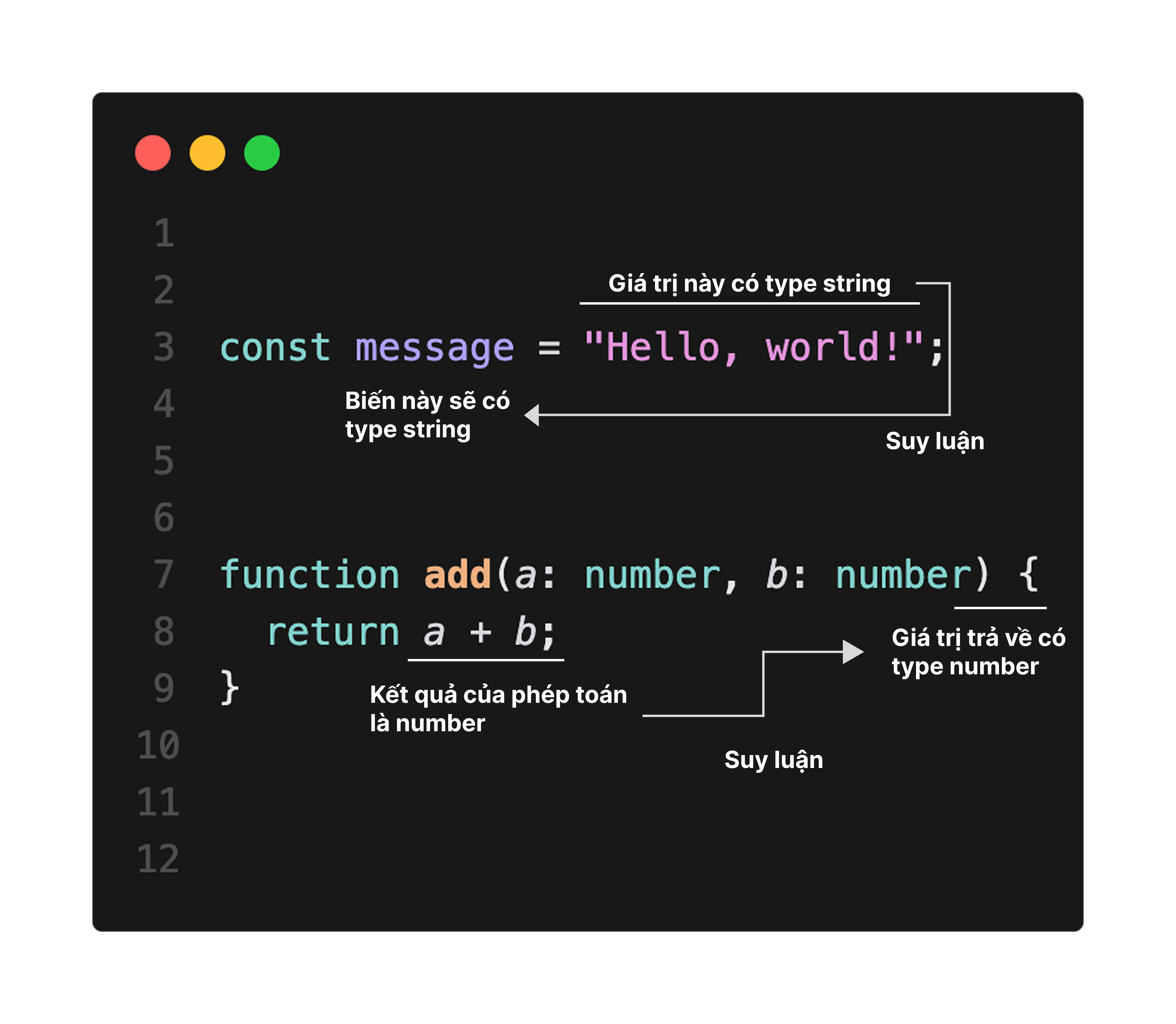
Type inference
- Khi kiểu của giá trị rõ ràng từ ngữ cảnh, kiểu sẽ được tự động suy luận. Cơ chế này gọi là type inference (suy luận kiểu).
- Nhờ type inference, developer có thể bỏ qua type annotation, giảm lượng code cần viết.
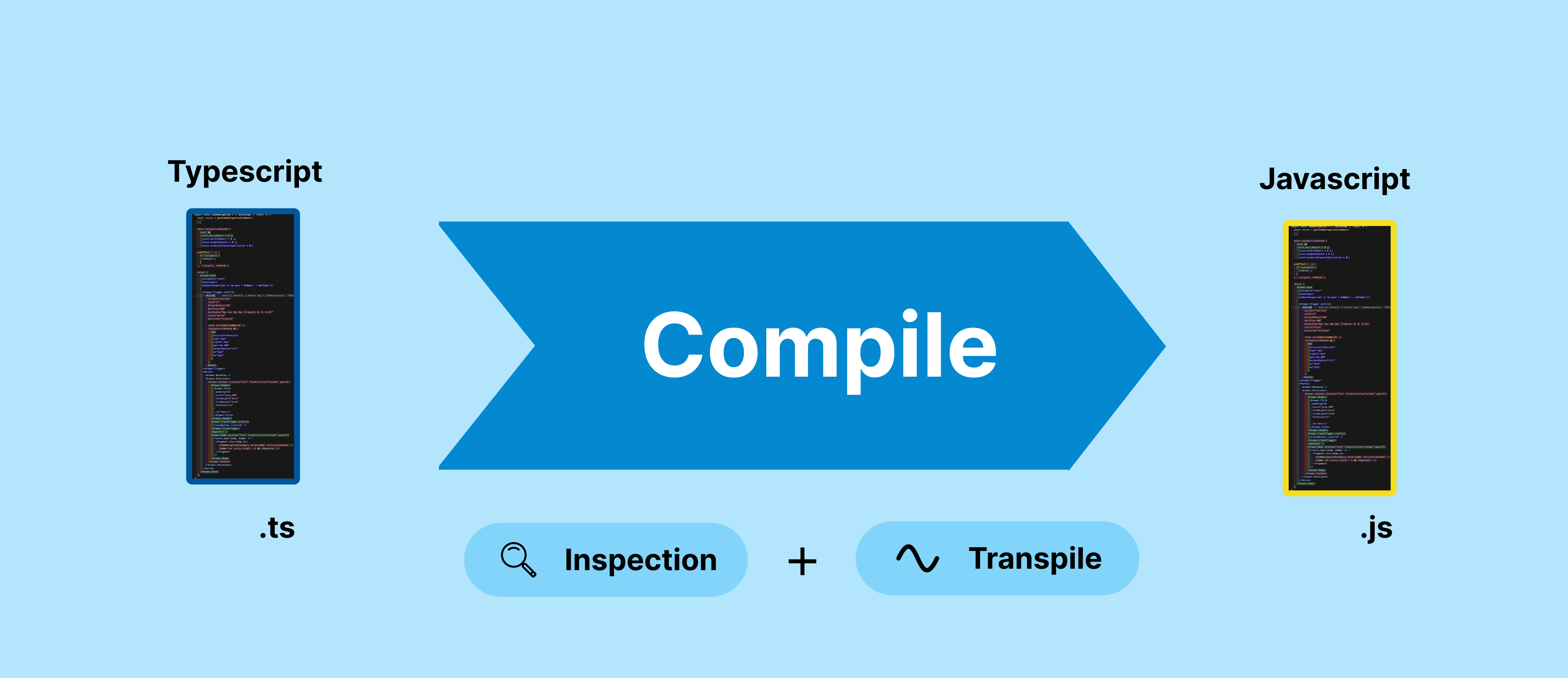
Compile
- Để chạy TypeScript, cần chuyển đổi sang JavaScript. Quá trình chuyển đổi này gọi là compile.
- Code JavaScript sau khi chuyển đổi có thể chạy trên browser hoặc server.
- Kiểm tra của TypeScript được thực hiện tại thời điểm compile.
Kiểu còn đóng góp cho documentation, refactoring và công cụ
- Là documentation: Thông tin kiểu đóng vai trò như documentation, giúp hiểu code.
- Refactoring an toàn: Khi thay đổi kiểu biến hoặc signature hàm, tất cả các vị trí cần sửa đều được phát hiện khi compile, giảm lỗi do sơ suất.
- Hỗ trợ công cụ phong phú: Hỗ trợ IDE và editor với kiểm tra lỗi realtime, auto-completion, refactoring tools, navigation.
» Tìm hiểu thêm về lý do sử dụng TypeScript
Nhiều editor hỗ trợ TypeScript
- Visual Studio Code
- JetBrains IDE (IntelliJ, WebStorm, PhpStorm, RubyMine, PyCharm, GoLand, v.v.)
- Vim
- NeoVim
- Emacs (Tide)
- Atom
- Sublime Text
» Tìm hiểu thêm về TypeScript và hệ sinh thái
Có thể tạo nhiều loại phần mềm
Phạm vi ứng dụng rộng là một trong những điểm hấp dẫn của TypeScript.
- Web application: Chiến trường chính của TypeScript. Được sử dụng rộng rãi trong phát triển frontend.
- Server-side application: Kết hợp với Node.js để phát triển backend hoặc API server.
- Mobile application: Sử dụng framework như React Native để phát triển ứng dụng mobile.
- Desktop application: Sử dụng Electron để phát triển ứng dụng desktop cross-platform.
- Cloud functions: Tạo serverless functions trên các nền tảng cloud như AWS Lambda hoặc Azure Functions.
- Utility và CLI tools: Phát triển command-line tools và các utility khác.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Sử dụng Pulumi hoặc AWS CDK để quản lý cấu hình infrastructure.
- Extension cho ứng dụng: Phát triển extension cho các ứng dụng desktop như Google Chrome hoặc Visual Studio Code bằng TypeScript.
» Tìm hiểu thêm về phạm vi ứng dụng của TypeScript
Cảm nhận của các công ty đã áp dụng TypeScript
- Slack: Dù codebase lớn, hệ thống kiểu vẫn đảm bảo tính an toàn và độ tin cậy.
- Airbnb: Nếu sử dụng TypeScript, có thể ngăn ngừa được 38% bug của Airbnb.
- Yahoo Japan: Kiểu tĩnh cải thiện chất lượng code và khả năng bảo trì, tích hợp với IDE tăng năng suất developer.
- LINE Corporation: Giảm chi phí QA cho những sửa đổi nhỏ nhờ TypeScript hóa.
- Sansan Corporation: Kiểu đóng vai trò như documentation, hữu ích cho việc đọc code và thay đổi code của team khác. Cũng là điểm thu hút trong tuyển dụng.
- Raksul Corporation: Được hưởng lợi từ hệ thống kiểu, auto-completion từ editor, dễ dàng tạo tình huống code = documentation.
Các kiểu cơ bản
Kiểu primitive
boolean: Giá trị boolean (true/false).number: Số.string: Chuỗi.bigint: Số nguyên lớn.symbol: Biểu thị giá trị duy nhất.undefined: Biểu thị trạng thái giá trị chưa được định nghĩa.null: Biểu thị trạng thái không có giá trị.
typescriptisReady : boolean = false;constage : number = 25;constfullName : string = "John Doe";constbigNumber : bigint = 100n;constuniqueSymbol : symbol =Symbol ("unique");constnotDefined : undefined =undefined ;constempty : null = null;
typescriptisReady : boolean = false;constage : number = 25;constfullName : string = "John Doe";constbigNumber : bigint = 100n;constuniqueSymbol : symbol =Symbol ("unique");constnotDefined : undefined =undefined ;constempty : null = null;
Kiểu đặc biệt
any: Kiểu có thể gán bất cứ thứ gì. Sử dụng khi không biết kiểu. Không có ràng buộc thao tác trên giá trị, tính an toàn kiểu yếu đi.unknown: Tương tự any, có thể gán bất cứ thứ gì. Thao tác trên giá trị bị hạn chế, tính an toàn kiểu được đảm bảo.void: Biểu thị không có giá trị. Sử dụng khi hàm không trả về gì.never: Biểu thị không bao giờ trả về gì. Sử dụng làm kiểu trả về cho hàm throw error hoặc vòng lặp vô hạn.
typescripta : any = 100; // Có thể gánconsole .log (a * 3); // Có thể thao tácconstx : unknown = 100; // Có thể gán'x' is of type 'unknown'.18046'x' is of type 'unknown'.console .log (* 3); // Không thể thao tác x // Hàm không có giá trị trả vềfunctiondoSomething (): void {}// Hàm không bao giờ trả về giá trịfunctionthrowError (): never {throw newError ();}
typescripta : any = 100; // Có thể gánconsole .log (a * 3); // Có thể thao tácconstx : unknown = 100; // Có thể gán'x' is of type 'unknown'.18046'x' is of type 'unknown'.console .log (* 3); // Không thể thao tác x // Hàm không có giá trị trả vềfunctiondoSomething (): void {}// Hàm không bao giờ trả về giá trịfunctionthrowError (): never {throw newError ();}
Type alias
- Type alias là tính năng định nghĩa kiểu có sẵn với tên mới.
- Hữu ích để biểu diễn kiểu phức tạp một cách đơn giản hoặc cải thiện khả năng đọc code.
typescriptStringOrNumber = string | number;letvalue :StringOrNumber ;value = "hello"; // Có thể gán kiểu stringvalue = 123; // Có thể gán kiểu number
typescriptStringOrNumber = string | number;letvalue :StringOrNumber ;value = "hello"; // Có thể gán kiểu stringvalue = 123; // Có thể gán kiểu number
Structural subtyping
- TypeScript áp dụng structural subtyping.
- Trong structural subtyping, việc gán biến được xác định dựa trên việc cấu trúc có tương thích hay không.
typescriptSummary = {name : string };typeDetail = {name : string;age : number };constjohnDetail :Detail = {name : "John",age : 28 };constsummary :Summary =johnDetail ; // Có thể gán vì tương thích structural subtypingconstjohnSummary :Summary = {name : "John" };constProperty 'age' is missing in type 'Summary' but required in type 'Detail'.2741Property 'age' is missing in type 'Summary' but required in type 'Detail'.: detail Detail =johnSummary ; // Không thể gán vì không tương thích structural subtyping (thiếu age)
typescriptSummary = {name : string };typeDetail = {name : string;age : number };constjohnDetail :Detail = {name : "John",age : 28 };constsummary :Summary =johnDetail ; // Có thể gán vì tương thích structural subtypingconstjohnSummary :Summary = {name : "John" };constProperty 'age' is missing in type 'Summary' but required in type 'Detail'.2741Property 'age' is missing in type 'Summary' but required in type 'Detail'.: detail Detail =johnSummary ; // Không thể gán vì không tương thích structural subtyping (thiếu age)
Array
Array literal
- Để tạo giá trị array, sử dụng array literal(
[]). - Có thể đặt giá trị khởi tạo array theo dạng
[phần tử 1, phần tử 2, ...].
typescriptnumbers = [1, 2, 3];
typescriptnumbers = [1, 2, 3];
Type annotation cho array
- Type annotation cho array sử dụng
tên_kiểu[]hoặcArray<tên_kiểu>.
typescriptnumbers : number[];letstrings :Array <string>;
typescriptnumbers : number[];letstrings :Array <string>;
Truy cập phần tử array
- Để truy cập phần tử array, sử dụng index.
- Chỉ định số nguyên bắt đầu từ 0 để lấy giá trị array và cũng có thể gán.
typescriptcolors = ["red", "green", "blue"];console .log (colors [0]);colors [1] = "yellow";console .log (colors );
typescriptcolors = ["red", "green", "blue"];console .log (colors [0]);colors [1] = "yellow";console .log (colors );
Readonly array
- Readonly array biểu thị array không thể thay đổi giá trị.
- Thêm
readonlyvào type annotation array để tạo readonly array. - Cũng có thể khai báo readonly array bằng
ReadonlyArray<tên_kiểu>, chức năng giống vớireadonly tên_kiểu[].
typescriptnumbers : readonly number[] = [1, 2, 3];conststrings :ReadonlyArray <string> = ["hello", "world"];Index signature in type 'readonly number[]' only permits reading.2542Index signature in type 'readonly number[]' only permits reading.numbers [0] = 4; // Không thể thay đổi giá trịProperty 'push' does not exist on type 'readonly string[]'.2339Property 'push' does not exist on type 'readonly string[]'.strings .("!"); // Không thể thêm phần tử push
typescriptnumbers : readonly number[] = [1, 2, 3];conststrings :ReadonlyArray <string> = ["hello", "world"];Index signature in type 'readonly number[]' only permits reading.2542Index signature in type 'readonly number[]' only permits reading.numbers [0] = 4; // Không thể thay đổi giá trịProperty 'push' does not exist on type 'readonly string[]'.2339Property 'push' does not exist on type 'readonly string[]'.strings .("!"); // Không thể thêm phần tử push
Lặp array
- Có cú pháp
for...ofđể lặp array.
typescriptnumbers = [1, 2, 3];for (constnum ofnumbers ) {console .log (num ); // In ra 1, 2, 3}
typescriptnumbers = [1, 2, 3];for (constnum ofnumbers ) {console .log (num ); // In ra 1, 2, 3}
Tuple type
- Sử dụng tuple type để cố định số lượng phần tử và kiểu của mỗi phần tử trong array.
- Kiểu được xác định cho mỗi index của phần tử.
typescripttuple : [string, number];tuple = ["hello", 10]; // Có thể gánType 'number' is not assignable to type 'string'.tuple = [10 ,"hello" ]; // Không thể gán vì thứ tự không đúng
Type 'string' is not assignable to type 'number'.2322
2322Type 'number' is not assignable to type 'string'.
Type 'string' is not assignable to type 'number'.Type '[string, number, string]' is not assignable to type '[string, number]'. Source has 3 element(s) but target allows only 2.2322Type '[string, number, string]' is not assignable to type '[string, number]'. Source has 3 element(s) but target allows only 2.= ["hello", 10, "world"]; // Không thể gán vì quá nhiều phần tử tuple
typescripttuple : [string, number];tuple = ["hello", 10]; // Có thể gánType 'number' is not assignable to type 'string'.tuple = [10 ,"hello" ]; // Không thể gán vì thứ tự không đúng
Type 'string' is not assignable to type 'number'.2322
2322Type 'number' is not assignable to type 'string'.
Type 'string' is not assignable to type 'number'.Type '[string, number, string]' is not assignable to type '[string, number]'. Source has 3 element(s) but target allows only 2.2322Type '[string, number, string]' is not assignable to type '[string, number]'. Source has 3 element(s) but target allows only 2.= ["hello", 10, "world"]; // Không thể gán vì quá nhiều phần tử tuple
Truy cập phần tử tuple
- Để truy cập phần tử tuple, cũng sử dụng index như array.
typescripttuple : [string, number] = ["hello", 10];console .log (tuple [0]);
typescripttuple : [string, number] = ["hello", 10];console .log (tuple [0]);
Object
Object literal
- Để tạo object, sử dụng object literal(
{}). - Có thể đặt giá trị khởi tạo object theo dạng
{ key: giá trị, ... }.
typescriptjohn = {name : "John",age : 20 };
typescriptjohn = {name : "John",age : 20 };
Property access
- Sử dụng dấu chấm
.để truy cập property của object.
typescriptconsole .log (john .name );
typescriptconsole .log (john .name );
Type annotation cho object
- Type annotation cho object được viết theo dạng
{property1: kiểu1, property2: kiểu2, ...}.
typescriptobj : {name : string;age : number };
typescriptobj : {name : string;age : number };
Readonly property
- Property có
readonlykhông thể gán.
typescriptobj : { readonlyname : string;age : number };obj = {name : "John",age : 20 };Cannot assign to 'name' because it is a read-only property.2540Cannot assign to 'name' because it is a read-only property.obj .= "Tom"; name
typescriptobj : { readonlyname : string;age : number };obj = {name : "John",age : 20 };Cannot assign to 'name' because it is a read-only property.2540Cannot assign to 'name' because it is a read-only property.obj .= "Tom"; name
Optional property
- Property có dấu
?(optional property) có thể bỏ qua.
typescriptobj : {name : string;age ?: number };obj = {name : "John" }; // Không có property `age` cũng không lỗi
typescriptobj : {name : string;age ?: number };obj = {name : "John" }; // Không có property `age` cũng không lỗi
Object method
- Có thể định nghĩa object có hàm làm property.
typescriptobj = {a : 1,b : 2,sum (): number {return this.a + this.b ;},};console .log (obj .sum ());
typescriptobj = {a : 1,b : 2,sum (): number {return this.a + this.b ;},};console .log (obj .sum ());
Index signature
- Object có thể sử dụng index signature để lấy giá trị với key bất kỳ.
- Type annotation cho index signature property được viết theo dạng
[tên_key: kiểu_key]: kiểu_giá_trị.
typescriptobj : { [key : string]: number };obj = {key1 : 1,key2 : 2 };console .log (obj ["key1"]);console .log (obj ["key2"]);
typescriptobj : { [key : string]: number };obj = {key1 : 1,key2 : 2 };console .log (obj ["key1"]);console .log (obj ["key2"]);
Shorthand property names
- Khi giá trị của property là biến đã được định nghĩa, có thể bỏ qua tên property đó (shorthand property names).
typescriptname = "John";constage = 20;constobj = {name ,age };console .log (obj );
typescriptname = "John";constage = 20;constobj = {name ,age };console .log (obj );
Optional chaining
- Khi không chắc property có tồn tại hay không, có thể truy cập an toàn bằng toán tử
?.(optional chaining).
typescriptprintLength (obj : {a ?: string }) {console .log (obj .a ?.length );}printLength ({a : "hello" });printLength ({});
typescriptprintLength (obj : {a ?: string }) {console .log (obj .a ?.length );}printLength ({a : "hello" });printLength ({});
Map
Map object
- Map object là collection ghép cặp key và value tương ứng.
- Key có thể là bất kỳ giá trị nào, kể cả object.
typescriptmap = newMap ();map .set ("name", "John");map .set ("age", "20");console .log (map .get ("name"));
typescriptmap = newMap ();map .set ("name", "John");map .set ("age", "20");console .log (map .get ("name"));
Type annotation cho Map
- Type annotation cho Map được viết theo dạng
Map<kiểu_key, kiểu_value>.
typescriptpeople :Map <string, number>;
typescriptpeople :Map <string, number>;
Lặp Map
- Khi lặp Map object bằng
for...of, mỗi entry được lấy theo thứ tự dưới dạng array gồm key và value. - Thứ tự phần tử được đảm bảo theo thứ tự thêm phần tử.
typescriptkey ,value ] ofmap ) {console .log (key ,value );}
typescriptkey ,value ] ofmap ) {console .log (key ,value );}
Set
Set object
- Set object là collection không có giá trị trùng lặp.
- Phần tử của Set có thể là bất cứ thứ gì.
typescriptset = newSet ();set .add (1);set .add (2);set .add (2); // Giá trị trùng không được thêm.console .log (set );
typescriptset = newSet ();set .add (1);set .add (2);set .add (2); // Giá trị trùng không được thêm.console .log (set );
Type annotation cho Set
- Type annotation cho Set được viết theo dạng
Set<kiểu_phần_tử>.
typescriptnumSet :Set <number>;
typescriptnumSet :Set <number>;
Lặp Set
- Set cũng có thể lặp bằng
for...ofnhư Map. - Thứ tự theo thứ tự
add.
typescriptvalue ofset ) {console .log (value );}
typescriptvalue ofset ) {console .log (value );}
Enum (Kiểu liệt kê)
Cơ bản về enum
- Enum định nghĩa tập hợp các giá trị số hoặc chuỗi liên quan.
- Enum được định nghĩa bằng từ khóa
enum.
typescriptColor {Red ,Green ,Blue ,}
typescriptColor {Red ,Green ,Blue ,}
Gán giá trị cho enum
- Giá trị của enum có thể chỉ định bằng string literal hoặc numeric literal.
typescriptColor {Red = "red",Green = "green",Blue = "blue",}
typescriptColor {Red = "red",Green = "green",Blue = "blue",}
Sử dụng enum
- Để truy cập từng giá trị của enum, sử dụng toán tử dấu chấm.
typescriptmyColor :Color =Color .Red ;
typescriptmyColor :Color =Color .Red ;
Union type
- Union type có thể biểu diễn giá trị nhận một trong nhiều kiểu.
- Sử dụng theo dạng
kiểu1 | kiểu2 | .... - Sử dụng khi muốn xử lý giá trị của nhiều kiểu khác nhau trong cùng một biến.
typescriptvalue : boolean | number;value = true; // Có thể gánvalue = 100; // Có thể gán
typescriptvalue : boolean | number;value = true; // Có thể gánvalue = 100; // Có thể gán
Discriminated union
- Discriminated union là union type đặc biệt có property kiểu literal chung.
- Có thể phân biệt kiểu bằng property chung.
typescriptTriangle = {kind : "triangle";base : number;height : number };typeRectangle = {kind : "rectangle";width : number;height : number };typeShape =Triangle |Rectangle ;functiongetArea (shape :Shape ): number {// Sử dụng property chung kind để xác định kiểuswitch (shape .kind ) {case "triangle":// Trong nhánh này shape được thu hẹp thành kiểu Trianglereturn (shape .base *shape .height ) / 2;case "rectangle":// Trong nhánh này shape được thu hẹp thành kiểu Rectanglereturnshape .width *shape .height ;}}
typescriptTriangle = {kind : "triangle";base : number;height : number };typeRectangle = {kind : "rectangle";width : number;height : number };typeShape =Triangle |Rectangle ;functiongetArea (shape :Shape ): number {// Sử dụng property chung kind để xác định kiểuswitch (shape .kind ) {case "triangle":// Trong nhánh này shape được thu hẹp thành kiểu Trianglereturn (shape .base *shape .height ) / 2;case "rectangle":// Trong nhánh này shape được thu hẹp thành kiểu Rectanglereturnshape .width *shape .height ;}}
Intersection type
- Intersection type định nghĩa kiểu mới kết hợp nhiều kiểu thành một.
- Sử dụng theo dạng
kiểu1 & kiểu2 & .... - Kiểu kết quả có tất cả property và method của mỗi kiểu.
typescriptOctopus = {swims : boolean };typeCat = {nightVision : boolean };typeOctocat =Octopus &Cat ;constoctocat :Octocat = {swims : true,nightVision : true };console .log (octocat );
typescriptOctopus = {swims : boolean };typeCat = {nightVision : boolean };typeOctocat =Octopus &Cat ;constoctocat :Octocat = {swims : true,nightVision : true };console .log (octocat );
Destructuring assignment
- Sử dụng destructuring assignment có thể gán từng phần tử của array vào biến cùng lúc (destructuring assignment cho array).
typescripta ,b ] = [1, 2];console .log (a );console .log (b );
typescripta ,b ] = [1, 2];console .log (a );console .log (b );
- Với destructuring assignment, có thể gán property của object vào các biến riêng lẻ (destructuring assignment cho object).
typescriptobj = {name : "John",age : 20,};const {name ,age } =obj ;console .log (name );console .log (age );
typescriptobj = {name : "John",age : 20,};const {name ,age } =obj ;console .log (name );console .log (age );
Rẽ nhánh điều kiện
- Trong TypeScript, giống JavaScript, có thể sử dụng câu lệnh
ifhoặcswitchđể rẽ nhánh điều kiện.
Câu lệnh if-else
typescriptage : number = 20;if (age >= 20) {console .log ("You are an adult.");} else {console .log ("You are a minor.");}
typescriptage : number = 20;if (age >= 20) {console .log ("You are an adult.");} else {console .log ("You are a minor.");}
Câu lệnh switch
typescriptcolor : string = "blue";switch (color ) {case "red":console .log ("Color is red.");break;case "blue":console .log ("Color is blue.");break;default:console .log ("Color is neither red nor blue.");}
typescriptcolor : string = "blue";switch (color ) {case "red":console .log ("Color is red.");break;case "blue":console .log ("Color is blue.");break;default:console .log ("Color is neither red nor blue.");}
Thu hẹp kiểu
- Sử dụng rẽ nhánh điều kiện, kiểu được tự động thu hẹp trong nhánh đó (Control flow analysis và type guard).
typescriptvalue : string | number;// Gán giá trị kiểu string hoặc number với xác suất 50%value =Math .random () < 0.5 ? "Hello" : 100;if (typeofvalue === "string") {// Trong nhánh này value được xử lý như kiểu stringconsole .log (value .toUpperCase ());} else {// Trong nhánh này value được xử lý như kiểu numberconsole .log (value * 3);}
typescriptvalue : string | number;// Gán giá trị kiểu string hoặc number với xác suất 50%value =Math .random () < 0.5 ? "Hello" : 100;if (typeofvalue === "string") {// Trong nhánh này value được xử lý như kiểu stringconsole .log (value .toUpperCase ());} else {// Trong nhánh này value được xử lý như kiểu numberconsole .log (value * 3);}
Function
- Trong TypeScript có thể thêm type annotation cho arrow function hoặc function declaration.
Arrow function
typescriptgreet = (name : string): string => {return `Hello ${name }`;};console .log (greet ("John"));
typescriptgreet = (name : string): string => {return `Hello ${name }`;};console .log (greet ("John"));
Function declaration
typescriptgreet (name : string): string {return `Hello ${name }`;}console .log (greet ("John"));
typescriptgreet (name : string): string {return `Hello ${name }`;}console .log (greet ("John"));
Destructuring parameter
- Có thể destructure array hoặc object literal làm tham số hàm (destructuring parameter).
typescriptprintCoord = ({x ,y }: {x : number;y : number }) => {console .log (`Coordinate is (${x }, ${y })`);};printCoord ({x : 10,y : 20 });
typescriptprintCoord = ({x ,y }: {x : number;y : number }) => {console .log (`Coordinate is (${x }, ${y })`);};printCoord ({x : 10,y : 20 });
Type guard function
- Sử dụng hàm xác định kiểu cụ thể (type guard function), kiểu sẽ được thu hẹp.
typescriptisString (value : any):value is string {return typeofvalue === "string";}functionprintLength (value : any) {if (isString (value )) {// Trong nhánh này value được xử lý như kiểu stringconsole .log (value .length );}}printLength ("hello");
typescriptisString (value : any):value is string {return typeofvalue === "string";}functionprintLength (value : any) {if (isString (value )) {// Trong nhánh này value được xử lý như kiểu stringconsole .log (value .length );}}printLength ("hello");
Optional parameter
- Có thể thêm
?vào tham số hàm để làm cho nó tùy chọn (optional parameter).
typescriptgreet (name ?: string) {if (name ===undefined ) {return "Hello!";} else {return `Hello ${name }!`;}}console .log (greet ("John"));console .log (greet ());
typescriptgreet (name ?: string) {if (name ===undefined ) {return "Hello!";} else {return `Hello ${name }!`;}}console .log (greet ("John"));console .log (greet ());
Default parameter
- Có thể đặt giá trị mặc định cho tham số hàm bằng
=(default parameter).
typescriptgreet (name : string = "Mystery") {return `Hello ${name }!`;}console .log (greet ("John"));console .log (greet ());
typescriptgreet (name : string = "Mystery") {return `Hello ${name }!`;}console .log (greet ("John"));console .log (greet ());
Rest parameter
- Có thể sử dụng
...để đặt rest parameter (số lượng tham số bất kỳ).
typescriptsum (...numbers : number[]) {returnnumbers .reduce ((total ,num ) =>total +num , 0);}console .log (sum (1, 2, 3, 4, 5));
typescriptsum (...numbers : number[]) {returnnumbers .reduce ((total ,num ) =>total +num , 0);}console .log (sum (1, 2, 3, 4, 5));
Class
Cú pháp class
- Cú pháp class của JavaScript có thể sử dụng như bình thường.
- Có thể thêm type annotation cho khai báo field.
typescriptPerson {name : string;age : number;constructor(name : string,age : number) {this.name =name ;this.age =age ;}introduce (): void {console .log (`My name is ${this.name } and I am ${this.age } years old.`);}}constjohn = newPerson ("John", 20);john .introduce ();
typescriptPerson {name : string;age : number;constructor(name : string,age : number) {this.name =name ;this.age =age ;}introduce (): void {console .log (`My name is ${this.name } and I am ${this.age } years old.`);}}constjohn = newPerson ("John", 20);john .introduce ();
Access modifier
- Có 3 access modifier:
public(mặc định),protected,private.
typescriptPerson {publicname : string;privateage : number;constructor(name : string,age : number) {this.name =name ;this.age =age ;}introduce (): void {console .log (`My name is ${this.name } and I am ${this.age } years old.`);}}constjohn = newPerson ("John", 20);console .log (john .name ); // In ra 'John'Property 'age' is private and only accessible within class 'Person'.2341Property 'age' is private and only accessible within class 'Person'.console .log (john .); // Lỗi (không thể truy cập vì private) age
typescriptPerson {publicname : string;privateage : number;constructor(name : string,age : number) {this.name =name ;this.age =age ;}introduce (): void {console .log (`My name is ${this.name } and I am ${this.age } years old.`);}}constjohn = newPerson ("John", 20);console .log (john .name ); // In ra 'John'Property 'age' is private and only accessible within class 'Person'.2341Property 'age' is private and only accessible within class 'Person'.console .log (john .); // Lỗi (không thể truy cập vì private) age
Readonly modifier trong class
- Property có
readonlymodifier là read-only. readonlymodifier có thể kết hợp với access modifier.
typescriptPerson {readonlyname : string;private readonlyage : number;constructor(name : string,age : number) {this.name =name ;this.age =age ;}introduce (): void {console .log (`My name is ${this.name } and I am ${this.age } years old.`);}}constjohn = newPerson ("John", 20);Cannot assign to 'name' because it is a read-only property.2540Cannot assign to 'name' because it is a read-only property.john .= "Tom"; // Lỗi (không thể thay đổi vì readonly) name
typescriptPerson {readonlyname : string;private readonlyage : number;constructor(name : string,age : number) {this.name =name ;this.age =age ;}introduce (): void {console .log (`My name is ${this.name } and I am ${this.age } years old.`);}}constjohn = newPerson ("John", 20);Cannot assign to 'name' because it is a read-only property.2540Cannot assign to 'name' because it is a read-only property.john .= "Tom"; // Lỗi (không thể thay đổi vì readonly) name
Constructor shorthand
- Trong TypeScript, thêm access modifier vào constructor parameter sẽ tự động định nghĩa field đó (constructor shorthand).
- Điều này giúp đơn giản hóa code.
typescriptPerson {constructor(publicname : string, privateage : number) {}introduce (): void {console .log (`My name is ${this.name } and I am ${this.age } years old.`);}}constjohn = newPerson ("John", 20);john .introduce ();
typescriptPerson {constructor(publicname : string, privateage : number) {}introduce (): void {console .log (`My name is ${this.name } and I am ${this.age } years old.`);}}constjohn = newPerson ("John", 20);john .introduce ();
Field initializer
- Có thể đặt giá trị khởi tạo trực tiếp khi khai báo field (field initializer).
typescriptCounter {count = 0; // Đặt giá trị khởi tạo là 0// ^^^initializerincrement (): void {this.count ++;}}constcounter = newCounter ();console .log (counter .count );counter .increment ();console .log (counter .count );
typescriptCounter {count = 0; // Đặt giá trị khởi tạo là 0// ^^^initializerincrement (): void {this.count ++;}}constcounter = newCounter ();console .log (counter .count );counter .increment ();console .log (counter .count );
Static field và static method
- Sử dụng từ khóa
staticcó thể định nghĩa field hoặc method liên quan đến class thay vì instance (static field, static method).
typescriptMyClass {staticx = 0;staticprintX (): void {console .log (MyClass .x );}}MyClass .printX ();
typescriptMyClass {staticx = 0;staticprintX (): void {console .log (MyClass .x );}}MyClass .printX ();
This type
- Trả về
thistrong method cho phép method chaining nối các lời gọi method (method chaining).
typescriptMyClass {value = 1;increment (): this {this.value ++;return this;}add (v : number): this {this.value +=v ;return this;}console .log (this.value );return this;}}newMyClass ().increment ().add (3).
typescriptMyClass {value = 1;increment (): this {this.value ++;return this;}add (v : number): this {this.value +=v ;return this;}console .log (this.value );return this;}}newMyClass ().increment ().add (3).
Kế thừa class
- Có thể kế thừa class bằng từ khóa
extends. - Giá trị property và method của superclass có thể truy cập từ subclass.
typescriptAnimal {name : string;constructor(name : string) {this.name =name ;}greet (): string {return `Hello, my name is ${this.name }`;}}classDog extendsAnimal {bark (): string {return "Woof!";}}constdog = newDog ("Max");console .log (dog .greet ());console .log (dog .bark ());
typescriptAnimal {name : string;constructor(name : string) {this.name =name ;}greet (): string {return `Hello, my name is ${this.name }`;}}classDog extendsAnimal {bark (): string {return "Woof!";}}constdog = newDog ("Max");console .log (dog .greet ());console .log (dog .bark ());
Toán tử instanceof
- Toán tử
instanceofcó thể xác định object có phải là instance của class cụ thể hay không.
typescriptAnimal {}classDog extendsAnimal {}constdog = newDog ();console .log (dog instanceofDog );console .log (dog instanceofAnimal );
typescriptAnimal {}classDog extendsAnimal {}constdog = newDog ();console .log (dog instanceofDog );console .log (dog instanceofAnimal );
Abstract class
- Có thể định nghĩa abstract class bằng từ khóa
abstract. - Abstract class không thể khởi tạo instance, được sử dụng làm base class cho các class khác kế thừa.
typescriptAnimal {abstractmakeSound (): void;move (): void {console .log ("roaming the earth...");}}classDog extendsAnimal {makeSound (): void {console .log ("Woof Woof");}}constdog = newDog ();dog .move ();dog .makeSound ();
typescriptAnimal {abstractmakeSound (): void;move (): void {console .log ("roaming the earth...");}}classDog extendsAnimal {makeSound (): void {console .log ("Woof Woof");}}constdog = newDog ();dog .move ();dog .makeSound ();
Getter và Setter
- Getter và setter là method để lấy/đặt property của object.
- Getter được định nghĩa bằng từ khóa
get, setter bằng từ khóaset.
typescriptCircle {private_radius : number;constructor(radius : number) {this._radius =radius ;}// Gettergetradius (): number {return this._radius ;}// Settersetradius (radius : number) {if (radius <= 0) {throw newError ("Invalid radius value");}this._radius =radius ;}}constcircle = newCircle (5);console .log (circle .radius );circle .radius = 3;console .log (circle .radius );circle .radius = -2;// Exception: 'Invalid radius value'
typescriptCircle {private_radius : number;constructor(radius : number) {this._radius =radius ;}// Gettergetradius (): number {return this._radius ;}// Settersetradius (radius : number) {if (radius <= 0) {throw newError ("Invalid radius value");}this._radius =radius ;}}constcircle = newCircle (5);console .log (circle .radius );circle .radius = 3;console .log (circle .radius );circle .radius = -2;// Exception: 'Invalid radius value'
Interface
- Interface của TypeScript có khả năng định nghĩa shape của property, method, class.
- Mục đích chính của sử dụng interface là bắt buộc class hoặc object cụ thể phải có property hoặc method cụ thể.
typescriptPrintable {}classMyClass implementsPrintable {console .log ("Hello, world!");}}
typescriptPrintable {}classMyClass implementsPrintable {console .log ("Hello, world!");}}
Cú pháp interface
- Interface của TypeScript có thể định nghĩa shape của object.
- Interface có thể mô tả signature của property và method.
typescriptPoint {readonlyx : number;readonlyy : number;sum (): number;}constpoint :Point = {x : 10,y : 20,sum : function () {return this.x + this.y ;},};
typescriptPoint {readonlyx : number;readonlyy : number;sum (): number;}constpoint :Point = {x : 10,y : 20,sum : function () {return this.x + this.y ;},};
Readonly modifier trong interface
- Có thể sử dụng readonly modifier trong interface để đặt property là read-only.
- Điều này khiến giá trị property không thể thay đổi sau khi được đặt.
typescriptPoint {readonlyx : number;readonlyy : number;}constp1 :Point = {x : 10,y : 20 };Cannot assign to 'x' because it is a read-only property.2540Cannot assign to 'x' because it is a read-only property.p1 .= 5; x
typescriptPoint {readonlyx : number;readonlyy : number;}constp1 :Point = {x : 10,y : 20 };Cannot assign to 'x' because it is a read-only property.2540Cannot assign to 'x' because it is a read-only property.p1 .= 5; x
Xử lý exception
- Trong TypeScript có thể sử dụng block try / catch / finally cho xử lý exception.
- Khi exception xảy ra (tức là throw error object), block catch được thực thi.
typescriptError ("An error occurred!");} catch (error ) {console .log (error );}
typescriptError ("An error occurred!");} catch (error ) {console .log (error );}
Cú pháp try-catch-finally
- Code trong block try phát hiện lỗi, block catch xử lý lỗi.
- Block finally được thực thi bất kể có lỗi hay không.
typescriptError ("Oops, something went wrong.");} catch (error ) {console .log (error );} finally {console .log ("This is the finally block. It always gets executed.");}
typescriptError ("Oops, something went wrong.");} catch (error ) {console .log (error );} finally {console .log ("This is the finally block. It always gets executed.");}
Exception class
- Trong TypeScript cũng có thể tạo custom error class.
- Có thể tạo error type cụ thể bằng custom class kế thừa Error class.
typescriptCustomError extendsError {code = "CustomError";constructor(message ?: string) {super(message );}}try {throw newCustomError ("This is a custom error");} catch (error ) {if (error instanceofCustomError ) {console .log (`${error .code }: ${error .message }`);}}
typescriptCustomError extendsError {code = "CustomError";constructor(message ?: string) {super(message );}}try {throw newCustomError ("This is a custom error");} catch (error ) {if (error instanceofCustomError ) {console .log (`${error .code }: ${error .message }`);}}
Xử lý bất đồng bộ
- TypeScript hỗ trợ lập trình bất đồng bộ, có thể xử lý hiệu quả các tác vụ tốn thời gian trong code.
Promise
- Promise biểu thị sự hoàn thành (hoặc thất bại) cuối cùng của thao tác bất đồng bộ và giá trị kết quả.
typescriptpromise = newPromise ((resolve ,reject ) => {setTimeout (() => {resolve ("Promise resolved");}, 2000);});promise .then ((data ) => {console .log (data );});
typescriptpromise = newPromise ((resolve ,reject ) => {setTimeout (() => {resolve ("Promise resolved");}, 2000);});promise .then ((data ) => {console .log (data );});
Cú pháp async/await
- Đã giới thiệu cú pháp async và cú pháp await để viết xử lý bất đồng bộ trực quan hơn.
- Sử dụng cú pháp async/await có thể viết code bất đồng bộ như thể là code đồng bộ.
typescriptdelay (ms : number) {return newPromise ((resolve ) =>setTimeout (resolve ,ms ));}async functionasyncFunction () {console .log ("Start");awaitdelay (2000);console .log ("End");}asyncFunction ();// Sau 2 giây
typescriptdelay (ms : number) {return newPromise ((resolve ) =>setTimeout (resolve ,ms ));}async functionasyncFunction () {console .log ("Start");awaitdelay (2000);console .log ("End");}asyncFunction ();// Sau 2 giây
Generics
- Sử dụng generics của TypeScript có thể tăng khả năng tái sử dụng kiểu và duy trì tính nhất quán của kiểu.
- Sử dụng generics có thể giới thiệu type variable, từ đó tổng quát hóa một phần chức năng.
typescriptidentity <T >(arg :T ):T {returnarg ;}// Gán string cho type variable Tconstoutput1 =identity <string>("myString");// Gán number cho type variable Tconstoutput2 =identity <number>(100);
typescriptidentity <T >(arg :T ):T {returnarg ;}// Gán string cho type variable Tconstoutput1 =identity <string>("myString");// Gán number cho type variable Tconstoutput2 =identity <number>(100);
Module
- Hệ thống module của TypeScript cho phép tách code chia sẻ với các module khác và code nội bộ của module (module).
greeter.tstypescriptgreet (name : string) {return `Hello, ${name }!`;}
greeter.tstypescriptgreet (name : string) {return `Hello, ${name }!`;}
main.tstypescriptgreet } from "./greeter";console .log (greet ("TypeScript"));
main.tstypescriptgreet } from "./greeter";console .log (greet ("TypeScript"));
import và export
- Để công khai hàm hoặc biến định nghĩa trong module ra bên ngoài, sử dụng export.
- Để sử dụng hàm hoặc biến mà module công khai, sử dụng import.
math.tstypescriptsquare (x : number) {returnx *x ;}export functioncube (x : number) {returnx *x *x ;}
math.tstypescriptsquare (x : number) {returnx *x ;}export functioncube (x : number) {returnx *x *x ;}
main.tstypescriptsquare ,cube } from "./math";console .log (square (2));console .log (cube (2));
main.tstypescriptsquare ,cube } from "./math";console .log (square (2));console .log (cube (2));
default export
- Sử dụng từ khóa default có nghĩa là module mặc định chỉ export một giá trị.
- default export có thể chỉ định alias khi import.
greeter.tstypescriptgreet (name : string) {return `Hello, ${name }!`;}
greeter.tstypescriptgreet (name : string) {return `Hello, ${name }!`;}
main.tstypescriptgreetFunction from "./greeter";console .log (greetFunction ("TypeScript"));
main.tstypescriptgreetFunction from "./greeter";console .log (greetFunction ("TypeScript"));
Re-export
- Module có thể re-export những gì được export từ module khác.
math.tstypescriptadd (x : number,y : number) {returnx +y ;}
math.tstypescriptadd (x : number,y : number) {returnx +y ;}
index.tstypescriptadd } from "./math";
index.tstypescriptadd } from "./math";
main.tstypescriptadd } from "./index";console .log (add (2, 3));
main.tstypescriptadd } from "./index";console .log (add (2, 3));
type import và type export
- Cũng có thể chỉ export/import kiểu.
types.tstypescriptMyObject = {name : string;age : number;};
types.tstypescriptMyObject = {name : string;age : number;};
main.tstypescriptMyObject } from "./types";// ^^^^type importconstobj :MyObject = {name : "TypeScript",age : 3,};
main.tstypescriptMyObject } from "./types";// ^^^^type importconstobj :MyObject = {name : "TypeScript",age : 3,};
Lập trình ở cấp độ kiểu
- TypeScript có nhiều tính năng để lập trình ở cấp độ kiểu như toán tử typeof, toán tử keyof, utility type.
Toán tử typeof
- Toán tử typeof có thể suy ra kiểu từ tên biến.
typescriptobject = {name : "TypeScript",version : 3.9,};typeObjectType = typeofobject ;
typescriptobject = {name : "TypeScript",version : 3.9,};typeObjectType = typeofobject ;
Toán tử keyof
- Sử dụng toán tử keyof có thể lấy tất cả key của object type dưới dạng union type của string literal.
typescriptPoint = {x : number;y : number;};typeKey = keyofPoint ;constkey1 :Key = "x"; // Gán OKconstkey2 :Key = "y"; // Gán OKconstType '"z"' is not assignable to type 'keyof Point'.2322Type '"z"' is not assignable to type 'keyof Point'.: key3 Key = "z"; // Không thể gán
typescriptPoint = {x : number;y : number;};typeKey = keyofPoint ;constkey1 :Key = "x"; // Gán OKconstkey2 :Key = "y"; // Gán OKconstType '"z"' is not assignable to type 'keyof Point'.2322Type '"z"' is not assignable to type 'keyof Point'.: key3 Key = "z"; // Không thể gán
type Key = keyof Point = "x" | "y".
Utility type
- TypeScript cung cấp nhiều thao tác kiểu phổ biến để tạo kiểu mới từ kiểu có sẵn.
Required
Requiredlà utility type biến optional property thành required property.
typescriptPerson = {name : string;age ?: number;};typeRequiredPerson =Required <Person >;// Chú ý age không còn là optional
typescriptPerson = {name : string;age ?: number;};typeRequiredPerson =Required <Person >;// Chú ý age không còn là optional
Partial
Partiallà utility type biến tất cả property của kiểu thành optional.
typescriptPerson = {name : string;age : number;};typeOptionalPerson =Partial <Person >;
typescriptPerson = {name : string;age : number;};typeOptionalPerson =Partial <Person >;
Readonly
Readonlylà utility type biến tất cả property của kiểu thành readonly. Các property đó không thể gán lại.
typescriptPerson = {name : string;age : number;};typeReadonlyPerson =Readonly <Person >;
typescriptPerson = {name : string;age : number;};typeReadonlyPerson =Readonly <Person >;
Record
Recordlà utility type đặt tất cả giá trị property của object thành kiểu cụ thể.
typescriptThreeLetterRecord =Record <"one" | "two" | "three", string>;
typescriptThreeLetterRecord =Record <"one" | "two" | "three", string>;
Pick
Picklà utility type chọn ra các property cụ thể từ object.
typescriptPerson = {name : string;age : number;address : string;};typePersonNameAndAge =Pick <Person , "name" | "age">;
typescriptPerson = {name : string;age : number;address : string;};typePersonNameAndAge =Pick <Person , "name" | "age">;
Omit
Omitlà utility type tạo kiểu bỏ đi property cụ thể từ object.
typescriptPerson = {name : string;age : number;address : string;};typePersonWithoutAddress =Omit <Person , "address">;
typescriptPerson = {name : string;age : number;address : string;};typePersonWithoutAddress =Omit <Person , "address">;
Exclude
Excludelà utility type loại bỏ kiểu cụ thể từ union type.
typescriptT1 = number | string | boolean;typeT2 =Exclude <T1 , boolean>;
typescriptT1 = number | string | boolean;typeT2 =Exclude <T1 , boolean>;
Extract
Extractlà utility type trích xuất phần chung của hai union type.
typescriptT1 = number | string | boolean;typeT2 = string | boolean;typeT3 =Extract <T1 ,T2 >;
typescriptT1 = number | string | boolean;typeT2 = string | boolean;typeT3 =Extract <T1 ,T2 >;
NonNullable
NonNullablelà utility type loại bỏ cả null và undefined từ kiểu có chứa chúng.
typescriptT1 = string | null | undefined;typeT2 =NonNullable <T1 >;
typescriptT1 = string | null | undefined;typeT2 =NonNullable <T1 >;
ReturnType
ReturnTypelà utility type lấy kiểu trả về của hàm.
typescriptstringify (value : number): string {return `${value }`;}typeStringifyReturnType =ReturnType <typeofstringify >;
typescriptstringify (value : number): string {return `${value }`;}typeStringifyReturnType =ReturnType <typeofstringify >;
Awaited
Awaitedlà utility type lấy kiểu giá trị trả về của Promise.
typescriptpromise1 =Promise .resolve ("data");constpromise2 =Promise .resolve (Promise .resolve ("data"));typeData1 =Awaited <typeofpromise1 >;typeData2 =Awaited <typeofpromise2 >;
typescriptpromise1 =Promise .resolve ("data");constpromise2 =Promise .resolve (Promise .resolve ("data"));typeData1 =Awaited <typeofpromise1 >;typeData2 =Awaited <typeofpromise2 >;
Mapped types
- Sử dụng Mapped types có thể tạo kiểu mới từ kiểu có sẵn.
- Mapped types "map" từng property của object để tạo object mới.
typescriptPerson = {name : string;age : number;};typeReadOnlyPerson = { readonly [K in keyofPerson ]:Person [K ] };
typescriptPerson = {name : string;age : number;};typeReadOnlyPerson = { readonly [K in keyofPerson ]:Person [K ] };
Indexed access type
- Sử dụng indexed access type có thể lấy kiểu của property trong kiểu.
typescriptPerson = {name : string;age : number;};typeName =Person ["name"];
typescriptPerson = {name : string;age : number;};typeName =Person ["name"];